UNIT 1 A
Unit -1
2 marks Questions.
1. What is Materials Science?
A. Materials science is a part of engineering that involves
discovering and designing new materials and analysing their properties and
structure. That information can then be used to make design choices. We can
also use our knowledge to break materials apart and recombine them in creative
ways. For example, did you know that nylon is created from oil? That kind of
thing wouldn't be possible without materials science.
2. When will interstitial solid
solution occur?
A. Interstitial solid solution is formed when atoms of small atomic
radius fit into the empty spaces or interstices of the lattice structure of the
solvent atoms as shown in Fig.
Since the empty spaces of the lattice structure are limited in size,
only atoms with atomic radius less than 1 angstrom are likely to form
interstitial solid solutions.
3. What is the difference between Schottky and
Frenkel defect?
A.
Schottky Defect
|
Frenkel Defect
|
1. Equal number of cations and anions are
missing from the lattice sites.
2. Found
in highly ionic compounds with high coordination numbers and where the
cations and anions are of similar size.
3. Density of the solid decreases
Examples: KBr, NaCl KCI
|
1. A cation leaves the normal lattice site and
occupies an interstitial site.
2. Found in ionic compounds with low
coordination numbers and where the anions are much larger in size than
cations.
3. Density of the solid remains the same.
Examples:Zns, AgBr
|
4. What are the advantages of magnetic
particle inspection?
A. Advantages of the Magnetic Particle method of
Non-Destructive Examination are:
•
It is quick and relatively
uncomplicated
•
It gives immediate indications of defects
It shows surface
and near surface defects, and these are the most serious ones as they
concentrate stresses
•
The method can be adapted for site or workshop use
•
It is inexpensive compared to radiography
•
Large or small objects can be examined
•
Elaborate pre-cleaning is
not necessary
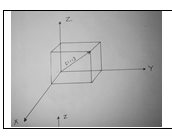
5. Draw the crystallographic
directions for following Miller indices:
(i) [1 1 1] (ii) [1 0 1]
A.
6. Draw the crystallographic directions for
following Miller indices:
(i) [1 0 0]
(ii) [0 1 1]
7. Draw the cubic
crystal planes for following Miller
indices:
(i) (1 0 1)
(ii) (1 1 1)
|
|








0 comments:
Post a Comment